
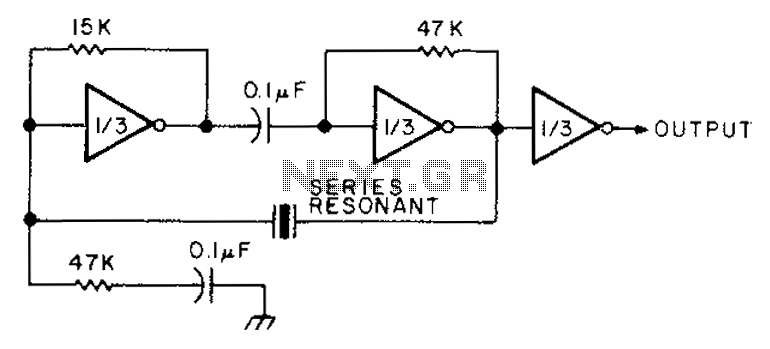
More so, the IEEE Standard 519 advises less than 5 percent THD for systems that connect to the power grid. In the meantime, the commercial power distribution grid is just less than 3 percent THD at the wave shape of the consumer’s connection point. For example, a 50 percent duty pulse square wave is like a sine wave of 48 percent THD. Popular kinds of inverters create quasi-square waves or square waves.Ī measure of the sine wave’s purity is the entire harmonic distortion (THD). Inverter Circuit Output WaveformsĪn inverter might create a modified sine wave, square wave output, and pulse width modulated wave, pulsed sine wave, output voltage waveform, or even sine wave based on the circuit design.
In the meantime, if additional inverters join together, an 18-step inverter obtains with another three inverters. The above diagram’s configuration is now popular in Alternating Current power supplies with an adjustable speed drive application. Meanwhile, rectifier circuits work in the inversion mode when controlled. In another vein, it’s vital to add that the current pulse number classifies Rectifier circuits and inverter pulse numbers, which flow to the Direct Current side of AC input voltage.įurthermore, the associated rectifier circuits can be 12-pulse rectifiers, 18-pulse rectifiers, or even more. For example, some assigned one-chip computers control the motor, which includes a PWM function pre-installed product.Ĭonsequently, it is feasible to produce a different frequency of pseudo sine waves while controlling the motor rotation speed by outlining the desired parameters.

The computer automatically controls the width of the pulse. The AC/DC conversion process will switch the power transistors like Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) while changing the OFF/ON intervals to produce pulse waves alongside diverse widths.Īfter that, it joins them to a quasi- sine wave known as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). Therefore, smoothing and exchanging the waveform near Direct Current.įurther, this simple inverter circuit will then output AC with varying frequency and voltage. Thus, to clean up, the capacitor would be discharged and charged repeatedly. Meanwhile, the rectification of full-wave alone can’t create smooth waveforms while the traces of rippled voltage and alternating current fluctuations would remain. To this end, its name is full-wave rectification since it transforms the negative and forward wave peaks. Therefore, the diode structure is made like a bridge to go through the negative peak via a forward way. This means the cycle’s other half will waste since it doesn’t negatively go to its peak. If the Direct current passes via the diode, it’s just the forward direction that will pass the electricity making the positive peak show. Thus, a diode helps pass electricity to convert it to a direct current, however not in a reverse direction. In other words, the magnitude and wave’s direction change regularly over time because the Alternating Current is a sine wave. It is effortless the converter circuit continuously converts Alternating Current to Direct Current under rectification.

In other words, it’s the device that changes DC (Direct Current) to AC (Alternating Current). Inverter circuit converts Direct Current electricity to Alternating Current to supply power to electricity grids or stand-out systems.
#Inverter transistor diagram how to#
Significantly, you will know how to make it in your home easily.Ī picture of an electronic diode component Meaning of Inverter Circuit However, read on to understand how to maximize inverter circuit benefits and to know everything about it. In addition, inverter power sources offer great additional or extra power supply following the growth in power electronic switching devices. The application of different electric power sources like DC battery storage alongside inverters is becoming common.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
